The desire of website operators to obtain as much information as possible about their users is as old as the internet itself. Simple counters for page views or the recognition of the web browser and screen resolution are the simplest applications of user tracking. Today, website operators are no longer solely dependent on Google to collect information about their visitors. There are sufficient free tools available to maintain their own tracking server. In this article, I will briefly discuss the historical background, technologies, and social aspects.
As more and more companies ventured into the vastness of the internet around the turn of the millennium, interest in finding out more about website visitors began. Initially, they were content with placing so-called visitor counters on the homepage. These visitor counters often displayed quite outrageous numbers. The ego of website operators certainly played a role, as many visitors to the homepage have an external impact and also make a certain impression on visitors. However, anyone who seriously wanted to make money through their website quickly realized that fictitious numbers didn’t generate revenue. So, more reliable methods were needed.
To prevent users from being counted multiple times each time they accessed the homepage, they began storing the IP address and setting a one-hour timeout before counting again. This was then called a reload block. Of course, this wasn’t a reliable detection method. At that time, connections over the telephone network were common via modem, and it often happened that the connection would drop, requiring a new connection. Then, a new IP address was also assigned. The accuracy of this solution therefore had a lot of potential for improvement.
When web space with PHP and MySQL databases became affordable around 2005, the trend shifted to storing visited pages in small text files called cookies in the browser. These analyses were already very informative and helped companies see which articles people were interested in. The only problem was when suspicious users deleted their cookies at every opportunity. Therefore, the trend shifted to storing all requests on the server, in so-called sessions. In most use cases, the accuracy achieved in this way is sufficient to better match supply to demand.
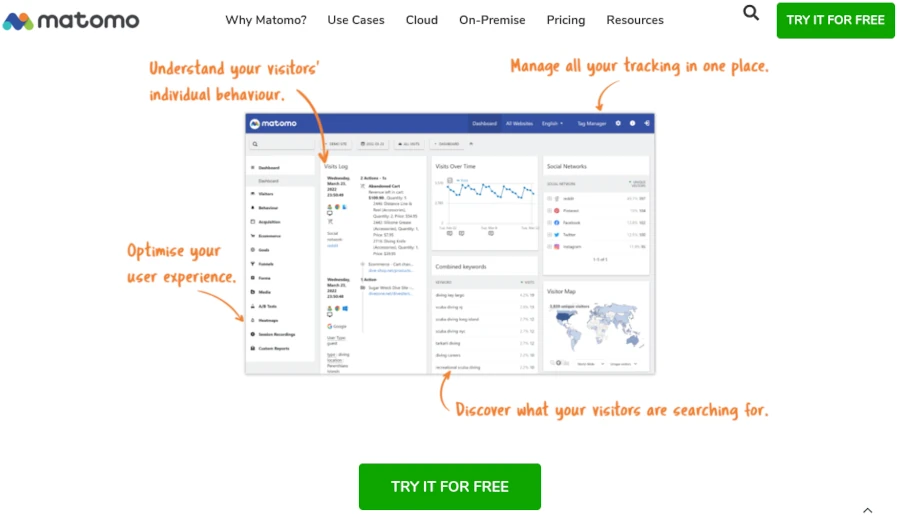
A popular tool for user tracking is Matomo, written in PHP. This self-hosted open source software allows you to bypass Google and also achieves better GDPR compliance, as the collected data is not shared with third parties. Furthermore, personalized data can be anonymized after a specified period of time, for example, at the beginning of the month. In this case, information such as IP addresses is replaced with random identifiers.
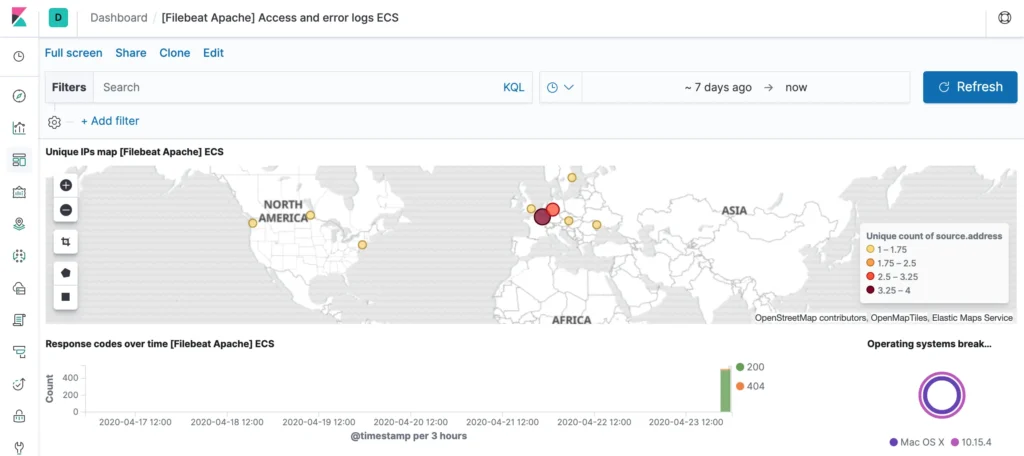
The whole issue is immediately taken to a whole new level when money is involved. In the past, it was companies that placed advertising banners on well-visited websites and then paid a small amount for every 1,000 ads. Nowadays, streaming services like Spotify or YouTube are interested in determining exactly how often a particular piece of content was viewed, or for how long a track was watched. Because the moment money is involved, there is a great interest in using small or large tricks to swindle a little more money than one is actually entitled to. This is precisely why companies like Google and Co. are constantly busy finding out how many users consume the content and for how long. In addition to tracking functions in the applications, these companies also use complex monitoring that can access original data from server logs and network traffic. This is where tools like the ELK stack or Prometheus and Grafana come into play.
Taking YouTube as an example, this service has several hurdles to overcome. Many people use YouTube as a TV replacement, as they can choose the content that interests them from a vast pool of content. A typical scenario is the automatic playback of ambient music for hours on end. If enough people do this without really paying attention to the content, it simply places a pointless burden on the server infrastructure and incurs considerable costs for the operator. This automatic autoplay function in the preview isn’t really interactive and is intended more as a teaser.
There are currently two strategies to keep users constantly engaged. One of these is short videos that run in a continuous loop until they manually move on to the next one. This allows you to mix in short advertising videos, but also to include news or opinion pieces. Of course, user tracking has to remove the repetitions during a monetized short on a continuous loop. This naturally leads to adjustments to the impression display. Another strategy used very excessively with long videos is disproportionately long ad breaks at relatively short intervals. This forces users to actively click away these ads each time, thus demanding attention.
Now, there are topics where services like YouTube, but also X or Facebook, have an interest in influencing their users in a certain direction. This could be the formation of opinions on political issues or simply commercialism. Now, one might think it would be a common strategy to suppress the visibility of undesirable opinions by adjusting the view count of the posts downwards. However, this wouldn’t be beneficial, because people have already seen the post. Therefore, a different strategy is much more effective. In the first step, the channel or post would be exempt from monetization, so the operator receives no additional compensation. In the next step, the number of views is increased, so that the content creator believes they are reaching a broad audience and takes fewer measures to gain more visibility. Additionally, using DevOps methods like A/B testing, feature flags, and load balancers, content views can be directed to posts only those who explicitly search for them. This avoids suspicion of censorship and significantly reduces visibility. Of course, unwanted posts only appear in recommendations for people who have explicitly subscribed to channels.

In the Netflix production “The Social Dilemma,” it is also lamented that bubbles are forming in which people with specific interests gather. This is an effect of so-called recommender systems. These recommenders are algorithms from the field of artificial intelligence. They function quite statically via statistical evaluations. Existing content is classified into categories, and then it is examined which groups of people are interested in a particular category and with what weighting. Content is then displayed accordingly, in proportion to the interests from that category. The content collected in this way can, of course, easily be marked with additional labels such as “well-suited” or “unsuitable.” Depending on the meta tags, unwanted content can then be buried in the depths of the database.
For all these measures to be effective, it is necessary to collect as much information about users as possible. This brings us back to user tracking. Tracking has become so sophisticated that browser settings that regularly delete cookies or the basic use of incognito mode are completely ineffective.
The only way to free yourself from dependence on the major platform providers is to consciously decide to no longer provide them with content. One step in this direction would be to operate your own website with appropriate monitoring for user tracking. Extensive content such as video and audio can be outsourced to several unknown platforms and embedded into the website. In this case, you should not upload all content to a single platform such as Odysee or Rumble, but rather cleverly distribute the content across multiple platforms without duplicating them. Such measures bind visitors to your own website and not to the respective platform operators.
Those with a little more financial freedom can also resort to free software such as PeerTube and host their own video platform. There are a number of options available here, but they require a great deal of effort and technical know-how from the operators.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.