When we look at images, we find those particularly aesthetically pleasing whose elements follow a specific ratio of lengths to areas. This principle of harmony is called the “Golden Ratio” and is widely used in nature.
One might think that in the age of graphics rendered by artificial intelligence, we no longer need the many fundamentals of graphic design. However, this is short-sighted, because on the one hand, we have to select the best option from the generated images. To make good decisions here, knowledge of proportions and aesthetics is essential. Furthermore, we must be able to clearly articulate our wishes in order to achieve an optimal result. Only things that we truly understand can we formulate clearly and unambiguously. Therefore, sound expertise is indispensable, especially when working with generative AI.
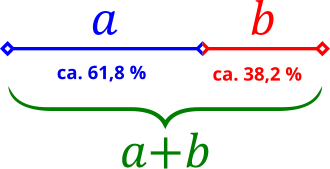
Geometrically, the Golden Ratio means that a line segment AB is divided into two segments of different lengths (a and b). If we now set a/b equal to the sum (a+b)/a, we obtain φ with the value 1.618. Incidentally, the exact value of φ is the square root of 5 (√5). The ratios of the lengths are approximately 3:2. The following graphic illustrates this relationship.
To apply the “Golden Ratio” to shapes, you don’t need to have passed advanced math courses in high school. All we need is the number φ. If we have a rectangle with a side length of one centimeter and multiply 1 by 1.618, we get 1.618. Now we can draw a rectangle with side lengths a = 1 and b = 1.618. The resulting ratio is perfect harmony and is called the “Golden Ratio.”
If we place our square with a side length of one centimeter inside this rectangle, we get a rectangular area B that can be divided according to the same pattern. If we repeat this process a few times, we get a tiled pattern. If we now draw an arc with a radius equal to the side length inside each of the resulting squares, we get a spiral. The shape in Figure 2 should already be familiar to most, and now you also know how it is created.
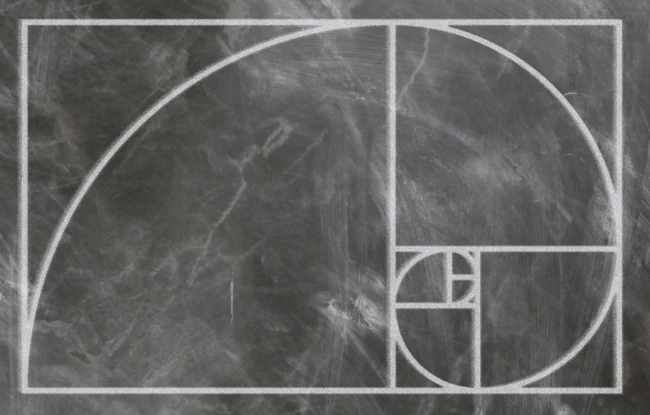

The spiral just described is also found in the so-called Fibonacci sequence. The Fibonacci sequence is a simple recursive addition of the two preceding numbers. Figure 3 shows how quickly the Fibonacci sequence can be calculated. As we can see, no advanced mathematical studies are necessary.
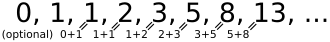

Where do we find the Golden Ratio used? Besides proportions in logos and other graphics, the Golden Ratio is often used in typography. The height ratios of small to large letters often follow a ratio of 1:1.618.
A typical scenario for applying the Golden Ratio is the positioning of objects within a graphic. To create a good illusion of depth, the objects need a corresponding ratio of heights to each other. But the way objects are positioned relative to each other also makes an image appear calm and harmonious or agitated and restless. So we have two ways of creating a mood in the viewer using the Golden Ratio. By deliberately disrupting the proportions, we achieve a certain restlessness, which can also be desirable. Such an inverted strategy can be used, for example, in advertising to stand out from the crowd and thus attract the viewer’s attention.