Tag Archives: Programming
References & Literature
Content | Apache Maven [en]
Index & Abbreviations
[A]
[B]
[C]
[D]
[E]
[F]
[G]
[H]
[I]
[J]
[K]
[L]
[M]
[N]
[O]
[P]
[Q]
[R]
[S]
[T]
[U]
[V]
[W]
[Y]
[Z]
[X]
return to the table of content: Apache Maven Master Class
A
- agiles Manifest
- (Apache) Ant
- Archetypen (archetypes)
B
C
D
- Deploy
- Docker Maven Image
- DRY – Don’t repeat yourself [2]
- DSL – Domain Specific Language
E
- EAR – Enterprise Archive
- EJB – Enterprise Java Beans
- Enforcer Plugin
- EoL – End of Live
F
G
- GAV Parameter [2]
- Goal [2]
- GPG – GNU Privacy Guard
H
I
- IDE – Integrierte Entwicklungsumgebung
- Installation (Linux / Windows)
- inkrementelle Builds
- (Apache) Ivy
J
- JAR – Java Archive
- jarsigner Plugin
- JDK – Java Development Kit
K
- Keytool (Java)
- KISS – Keep it simple, stupid.
- Kochbuch: Maven Codebeispiele
L
M
N
O
- OWASP – Open Web Application Security Project [2]
P
- Plugin
- Production Candidate
- POM – Project Object Model
- Maven Properties
- Prozess
Q
R
S
T
- target – Verzeichnis
- Token Replacement
U
V
W
- WAR – Web Archive
X
Y
Z
[A]
[B]
[C]
[D]
[E]
[F]
[G]
[H]
[I]
[J]
[K]
[L]
[M]
[N]
[O]
[P]
[Q]
[R]
[S]
[T]
[U]
[V]
[W]
[Y]
[Z]
[X]
return to the table of content: Apache Maven Master Class
Apache Maven Master Class
Apache Maven (Maven for short) was first released on March 30, 2002, as an Apache Top-Level Project under the free Apache 2.0 License. This license also allows free use by companies in a commercial environment without paying license fees.
The word Maven comes from Yiddish and means something like “collector of knowledge.”
Maven is a pure command-line program developed in the Java programming language. It belongs to the category of build tools and is primarily used in Java software development projects. In the official documentation, Maven describes itself as a project management tool, as its functions extend far beyond creating (compiling) binary executable artifacts from source code. Maven can be used to generate quality analyses of program code and API documentation, to name just a few of its diverse applications.
Benefits
- Access to all subscription articles
- Accessing the Maven Sample Git Repository
- Regular updates
- Email support
- Regular live video FAQs
- Video workshops
- Submit your own topic suggestions
- 30% discount on Maven training
Target groups
This online course is suitable for both beginners with no prior knowledge and experienced experts. Each lesson is self-contained and can be individually selected. Extensive supplementary material explains concepts and is supported by numerous references. This allows you to use the Apache Maven Master Class course as a reference. New content is continually being added to the course. If you choose to become an Apache Maven Master Class member, you will also have full access to exclusive content.

Developer
- Maven Basics
- Maven on the Command Line
- IDE Integration
- Archetypes: Creating Project Structures
- Test Integration (TDD & BDD) with Maven
- Test Containers with Maven
- Multi-Module Projects for Microservices

Build Manager / DevOps
- Release Management with Maven
- Deploy to Maven Central
- Sonatype Nexus Repository Manager
- Maven Docker Container
- Creating Docker Images with Maven
- Encrypted Passwords
- Process & Build Optimization

Quality Manager
- Maven Site – The Reporting Engine
- Determine and evaluate test coverage
- Static code analysis
- Review coding style specifications
Cookbook: Maven Source Code Samples
Our Git repository contains an extensive collection of various code examples for Apache Maven projects. Everything is clearly organized by topic.
Back to table of contents: Apache Maven Master Class
- Token Replacement
- Compiler Warnings
- Excecutable JAR Files
- Enforcments
- Unit & Integration Testing
- Multi Module Project (JAR / WAR)
- BOM – Bill Of Materials (Dependency Management)
- Running ANT Tasks
- License Header – Plugin
- OWASP
- Profiles
- Maven Wrapper
- Shade Ueber JAR (Plugin)
- Java API Documantation (JavaDoc)
- Java Sources & Test Case packaging into JARs
- Docker
- Assemblies
- Maven Reporting (site)
- Flatten a POM
- GPG Signer
02. Build Management & DevOps
01. Fundamentals
Vibe coding – a new plague of the internet?
When I first read the term vibe coding, I first thought of headphones, chill music and transitioning into flow. The absolute state of creativity that programmers chase. A rush of productivity. But no, it became clear to me quite quickly that it was about something else.
Vibe coding is the name given to what you enter into an AI via the prompt in order to get a usable program. The output of the Large Language Model (LLM) is not yet the executable program, but rather just the corresponding source text in the programming language that the Vibe Coder specifies. Therefore, depending on which platform it is on, the Vibe Coder still needs the ability to make the whole thing work.
Since I’ve been active in IT, the salespeople’s dream has been there: You no longer need programmers to develop applications for customers. So far, all approaches of this kind have been less than successful, because no matter what you did, there was no solution that worked completely without programmers. A lot has changed since the general availability of AI systems and it is only a matter of time before LLM systems such as Copilot etc. also deliver executable applications.
The possibilities that Vibe Coding opens up are quite remarkable if you know what you are doing. Straight from Goethe’s sorcerer’s apprentice, who was no longer able to master the spirits he summoned. Are programmers now becoming obsolete? In the foreseeable future, I don’t think the programming profession will die out. But a lot will change and the requirements will be very high.
I can definitely say that I am open to AI assistance in programming. However, my experiences so far have taught me to be very careful about what the LLMs suggest as a solution. Maybe it’s because my questions were very specific and for specific cases. The answers were occasionally a pointer in a possible direction that turned out to be successful. But without your own specialist knowledge and experience, all of the AI’s answers would not have been usable. Justifications or explanations should also be treated with caution in this context.
There are now various offers that want to teach people how to use artificial intelligence. So in plain language, how to formulate a functioning prompt. I think such offers are dubious, because the LLMs were developed to understand natural (human) language. So what should you learn to formulate complete and understandable sentences?
Anyone who creates an entire application using Vibe Coding must test it extensively. So click through the functions and see if everything works as it should. This can turn into a very annoying activity that becomes more annoying with each run.
The use of programs created by Vibe Coding is also unproblematic as long as they run locally on your own computer and are not freely accessible as a commercial Internet service. Because this is exactly where the danger lurks. The programs created by Vibe Coding are not sufficiently protected against hacker attacks, which is why they should only be operated in closed environments. I can also well imagine that in the future the use of programs that are Vibe Coded will be prohibited in security-critical environments such as authorities or banks. As soon as the first cyber attacks on company networks through Vibe coding programs become known, the bans are in place.
Besides the question of security for Vibe Coding applications, modifications and extensions will be extremely difficult to implement. This phenomenon is well-known in software development and occurs regularly with so-called legacy applications. As soon as you hear that something has grown organically over time, you’re already in the thick of it. A lack of structure and so-called technical debt cause a project to erode over time to such an extent that the impact of changes on the remaining functionality becomes very difficult to assess. It is therefore likely that there will be many migration projects in the future to convert AI-generated codebases back into clean structures. For this reason, Vibe Coding is particularly suitable for creating prototypes to test concepts.

There are now also complaints in open source projects that every now and then there are contributions that convert almost half of the code base and add faulty functions. Of course, common sense and the many standards established in software development help here. It’s not like we haven’t had experience with bad code commits in open source before. This gave rise to the dictatorship workflow for tools like Git, which was renamed Pull Request by the code hosting platform GitHub.
So how can you quickly identify bad code? My current prescription is to check test coverage for added code. No testing, no code merge. Of course, test cases can also be Vibe Coded or lack necessary assertions, which can now also be easily recognized automatically. In my many years in software development projects, I’ve experienced enough that no Vibe Coder can even come close to bringing beads of sweat to my forehead.
My conclusion on the subject of Vibe Coding is: In the future, there will be a shortage of capable programmers who will be able to fix tons of bad production code. So it’s not a dying profession in the foreseeable future. On the other hand, a few clever people will definitely script together a few powerful isolated solutions for their own business with simple IT knowledge that will lead to competitive advantages. As we experience this transformation, the Internet will continue to become cluttered and the gems Weizenbaum once spoke of will become harder to find.
Featureitis
You don’t have to be a software developer to recognize a good application. But from my own experience, I’ve often seen programs that were promising and innovative at the start mutate into unwieldy behemoths once they reach a certain number of users. Since I’ve been making this observation regularly for several decades now, I’ve wondered what the reasons for this might be.
The phenomenon of software programs, or solutions in general, becoming overloaded with details was termed “featuritis” by Brooks in his classic book, “The Mythical Man-Month.” Considering that the first edition of the book was published in 1975, it’s fair to say that this is a long-standing problem. Perhaps the most famous example of featureitis is Microsoft’s Windows operating system. Of course, there are countless other examples of improvements that make things worse.
The phenomenon of software programs, or solutions in general, becoming overloaded with details is what Brooks called “featuritis.” Windows users who were already familiar with Windows XP and then confronted with its wonderful successor Vista, only to be appeased again by Windows 7, and then nearly had a heart attack with Windows 8 and 8.1, were calmed down again at the beginning of Windows 10. At least for a short time, until the forced updates quickly brought them back down to earth. And don’t even get me started on Windows 11. The old saying about Windows was that every other version is junk and should be skipped. Well, that hasn’t been true since Windows 7. For me, Windows 10 was the deciding factor in completely abandoning Microsoft, and like many others, I bought a new operating system. Some switched to Apple, and those who couldn’t afford or didn’t want the expensive hardware, like me, opted for a Linux system. This shows how a lack of insight can quickly lead to the loss of significant market share. Since Microsoft isn’t drawing any conclusions from these developments, this fact seems to be of little concern to the company. For other companies, such events can quickly push them to the brink of collapse, and beyond.
One motivation for adding more and more features to an existing application is the so-called product life cycle, which is represented by the BCG matrix in Figure 1.
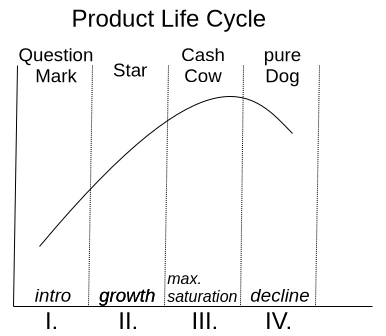
With a product’s launch, it’s not yet certain whether it will be accepted by the market. If users embrace it, it quickly rises to stardom and reaches its maximum market position as a cash cow. Once market saturation is reached, it degrades to a slow seller. So far, so good. Unfortunately, the prevailing management view is that if no growth is generated compared to the previous quarter, market saturation has already been reached. This leads to the nonsensical assumption that users must be forced to accept an updated version of the product every year. Of course, the only way to motivate a purchase is to print a bulging list of new features on the packaging.
Since well-designed features can’t simply be churned out on an assembly line, a redesign of the graphical user interface is thrown in as a free bonus every time. Ultimately, this gives the impression of having something completely new, as it requires a period of adjustment to discover the new placement of familiar functions. It’s not as if the redesign actually streamlines the user experience or increases productivity. The arrangement of input fields and buttons always seems haphazardly thrown together.
But don’t worry, I’m not calling for an update boycott; I just want to talk about how things can be improved. Because one thing is certain: thanks to artificial intelligence, the market for software products will change dramatically in just a few years. I don’t expect complex and specialized applications to be produced by AI algorithms anytime soon. However, I do expect that these applications will have enough poorly generated AI-generated code sequences, which the developer doesn’t understand, injected into their codebases, leading to unstable applications. This is why I’m rethinking clean, handcrafted, efficient, and reliable software, because I’m sure there will always be a market for it.
I simply don’t want an internet browser that has mutated into a communication hub, offering chat, email, cryptocurrency payments, and who knows what else, in addition to simply displaying web pages. I want my browser to start quickly when I click something, then respond quickly and display website content correctly and promptly. If I ever want to do something else with my browser, it would be nice if I could actively enable this through a plugin.
Now, regarding the problem just described, the argument is often made that the many features are intended to reach a broad user base. Especially if an application has all possible options enabled from the start, it quickly engages inexperienced users who don’t have to first figure out how the program actually works. I can certainly understand this reasoning. It’s perfectly fine for a manufacturer to focus exclusively on inexperienced users. However, there is a middle ground that considers all user groups equally. This solution isn’t new and is very well-known: the so-called product lines.
In the past, manufacturers always defined target groups such as private individuals, businesses, and experts. These user groups were then often assigned product names like Home, Enterprise, and Ultimate. This led to everyone wanting the Ultimate version. This phenomenon is called Fear Of Missing Out (FOMO). Therefore, the names of the product groups and their assigned features are psychologically poorly chosen. So, how can this be done better?
An expert focuses their work on specific core functions that allow them to complete tasks quickly and without distractions. For me, this implies product lines like Essentials, Pure, or Core.
If the product is then intended for use by multiple people within the company, it often requires additional features such as external user management like LDAP or IAM. This specialized product line is associated with terms like Enterprise, Company, Business, and so on.
The cluttered end result, actually intended for NOOPS, has all sorts of things already activated during installation. If people don’t care about the application’s startup and response time, then go for it. Go all out. Throw in everything you can! Here, names like Ultimate, Full, and Maximized Extended are suitable for labeling the product line. The only important thing is that professionals recognize this as the cluttered version.
Those who cleverly manage these product lines and provide as many functions as possible via so-called modules, which can be installed later, enable high flexibility even in expert mode, where users might appreciate the occasional additional feature.
If you install tracking on the module system beforehand to determine how professional users upgrade their version, you’ll already have a good idea of what could be added to the new version of Essentials. However, you shouldn’t rely solely on downloads as the decision criterion for this tracking. I often try things out myself and delete extensions faster than the installation process took if I think they’re useless.
I’d like to give a small example from the DevOps field to illustrate the problem I just described. There’s the well-known GitLab, which was originally a pure code repository hosting project. The name still reflects this today. An application that requires 8 GB of RAM on a server in its basic installation just to make a Git repository accessible to other developers is unusable for me, because this software has become a jack-of-all-trades over time. Slow, inflexible, and cluttered with all sorts of unnecessary features that are better implemented using specialized solutions.
In contrast to GitLab, there’s another, less well-known solution called SCM-Manager, which focuses exclusively on managing code repositories. I personally use and recommend SCM-Manager because its basic installation is extremely compact. Despite this, it offers a vast array of features that can be added via plugins.
I tend to be suspicious of solutions that claim to be an all-in-one solution. To me, that’s always the same: trying to do everything and nothing. There’s no such thing as a jack-of-all-trades, or as we say in Austria, a miracle worker!
When selecting programs for my workflow, I focus solely on their core functionality. Are the basic features promised by the marketing truly present and as intuitive as possible? Is there comprehensive documentation that goes beyond a simple “Hello World”? Does the developer focus on continuously optimizing core functions and consider new, innovative concepts? These are the questions that matter to me.
Especially in commercial environments, programs are often used that don’t deliver on their marketing promises. Instead of choosing what’s actually needed to complete tasks, companies opt for applications whose descriptions are crammed with buzzwords. That’s why I believe that companies that refocus on their core competencies and use highly specialized applications for them will be the winners of tomorrow.